Happy Horse 1L
- Courier collects weekdays at 12pm

WEATHERBEETA SIZE CHARTS
DUBLIN SIZE CHARTS


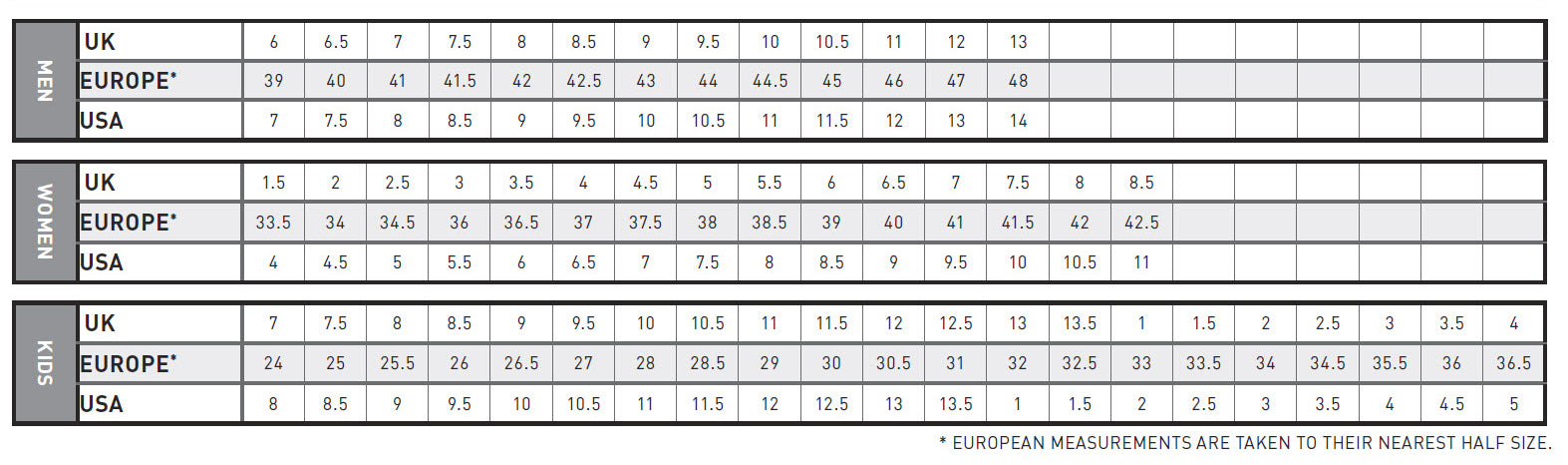
ARIAT SIZE CHARTS
BARE EQUESTRIAN SIZE CHART
PS of SWEDEN SIZE CHARTS
PS of Sweden - Saddle Blankets Size Guide
- Low stock - 1 item left
- Backordered, shipping soon
Happy Horse Ingredients:
Choline
Choline is a B group vitamin that acts as a lipotropic agent to aid in the prevention of fat accumulation in the liver (Marks, 2012). If choline is deficient fatty liver can result, which leaves the horse with increased concentrations of triglycerides in the liver. Choline helps eliminate poisons from the system through the liver.
Niacin
Is important in the metabolic process to ensure healthy skin as well as proper function of the digestive tract (Marks, 2012) Niacin is produced in the horses’ gastrointestinal tract by microbes. Niacin is also produced by the body from the amino acid tryptophan, however many cereal grains contain high levels of leucine which interfere (Lewis, 1995) with the conversion of niacin to tryptophan, so supplementation is a good idea. Niacin has been known for its ability to increase blood flow to extremities and improved blood circulation. Methionine is an essential amino acid required for proper hoof protein development. Research has shown that sulphur-bearing amino acids play an important role in the proteins of the equine hoof wall (Grosebaugh and Hood, 1992) methionine is the most important amino acid for
hoof growth. It works with choline to fight against tumours and helps prevent oedema and infection. Methionine scavenges free radicals and has a detoxifying action.
Carnitine
Enhances ATP production in the muscle and is essential for the transport of fats into the mitochondria where they are burnt to produce energy. Carnitine prevents toxic overload and is useful to delay the onset of exercise induced metabolic acidosis and fatigue development. Carnitine is essential for normal heart function and useful to help prevent muscle damage after vigorous exercise. Maltodextrines and Mollases are both a useful source of readily available energy.
References
Grosenbaugh, D. A., & Hood, D. M. (1992). Keratin and associated proteins of the equine
hoof wall. American journal of veterinary research, 53(10), 1859-1863.
Lewis, L. D. (1995). Equine clinical nutrition: feeding
Feeding Instructions: Give 1 Litre daily for 2-3 days
Our website is fully stock controlled, so if you can add it to your cart we have it in stock.
Couier is picked up weekdays at 12pm.
Click and collect avaliable after hours.